[Baekjoon/C++] 11650번 좌표 정렬하기
문제 설명
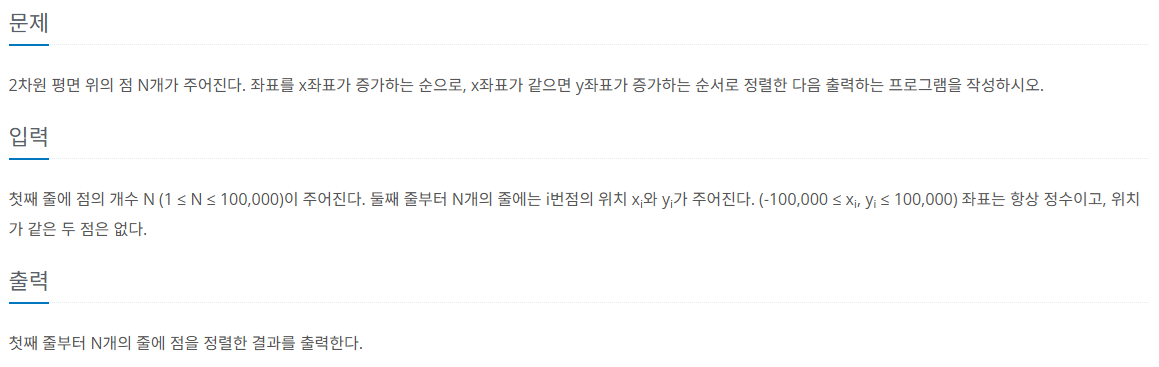
입출력 예
코드 구현 1
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int N=0, xy=0;
cin >> N;
vector<vector<int>> vec(N, vector<int>(2));
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){ //N개 행
vector<int> tvec; //새로운 행 생성
for(int j=0; j<2; j++){ //각 행에 2열
cin >> xy;
tvec.push_back(xy);
}
vec.push_back(tvec); //완성된 행을 2차원 벡터에 추가
}
for(int i=0; i<N-1; i++){ //(x,y)에서 x오름차순
for(int j=1; j<N-i; j++){ //버블정렬 방식 O(N²)
if(vec[i+j-1][0]>vec[i+j][0]){
swap(vec[i+j-1], vec[i+j]); //행 교환
}
}
}
for(int i=1; i<N; i++){ //y오름차순
if(vec[i-1][0]==vec[i][0]){
if(vec[i-1][1]>vec[i][1]){
swap(vec[i-1][1], vec[i][1]);
}
}
}
for(vector<int> row: vec){
for(int val: row){
cout << val << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
버블정렬을 사용해서 풀어봤는데 시간초과가 떴다.
코드 구현 2
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int N=0;
cin >> N;
vector<vector<int>> vec(N, vector<int>(2));
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
cin >> vec[i][0] >> vec[i][1];
}
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b){
if(a[0]==b[0]){
return a[1]<b[1]; //첫번째 열 같으면 두번째 열을 기준으로 정렬
}
return a[0]<b[0]; //첫번째 열 기준으로 정렬
});
for(vector<int> row: vec){
cout << row[0] << " " << row[1] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
코드구현1에서 버블정렬(시간복잡도 O(N²))을 사용하여 시간이 초과된 것 같아 구현2에서는 sort를 사용하여 시간복잡도를 O(NlogN)로 줄였지만 마찬가지로 시간초과가 나왔다.
마지막줄에 endl 대신 “\n”로 변경해주니 시간초과가 해결됐다.
최종코드
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int N=0;
cin >> N;
vector<vector<int>> vec(N, vector<int>(2));
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
cin >> vec[i][0] >> vec[i][1];
}
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b){
if(a[0]==b[0]){
return a[1]<b[1]; //첫번째 열 같으면 두번째 열을 기준으로 정렬
}
return a[0]<b[0]; //첫번째 열 기준으로 정렬
});
for(vector<int> row: vec){
cout << row[0] << " " << row[1] << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
Review
- endl: 출력 후 줄바꿈을 하고, 그 후 buffer flush한다.
- Buffer flush: 출력 버퍼에 쌓인 데이터를 즉시 화면에 출력하는 작업.
- 추가적인 시간과 리소스를 소모하게 된다.
- “\n”: 단순한 줄바꿈만 한다.
- 출력 후 buffer flush하지 않기 때문에 endl에 비해 빠르다.
- 버퍼가 가득 차거나 flush를 명시적으로 호출하지 않는 한, 프로그램이 종료되거나 출력이 완료될 때 한번에 버퍼를 flush한다.
출처: 백준, https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11650
