[Baekjoon/C++] 7576번 토마토
문제 설명

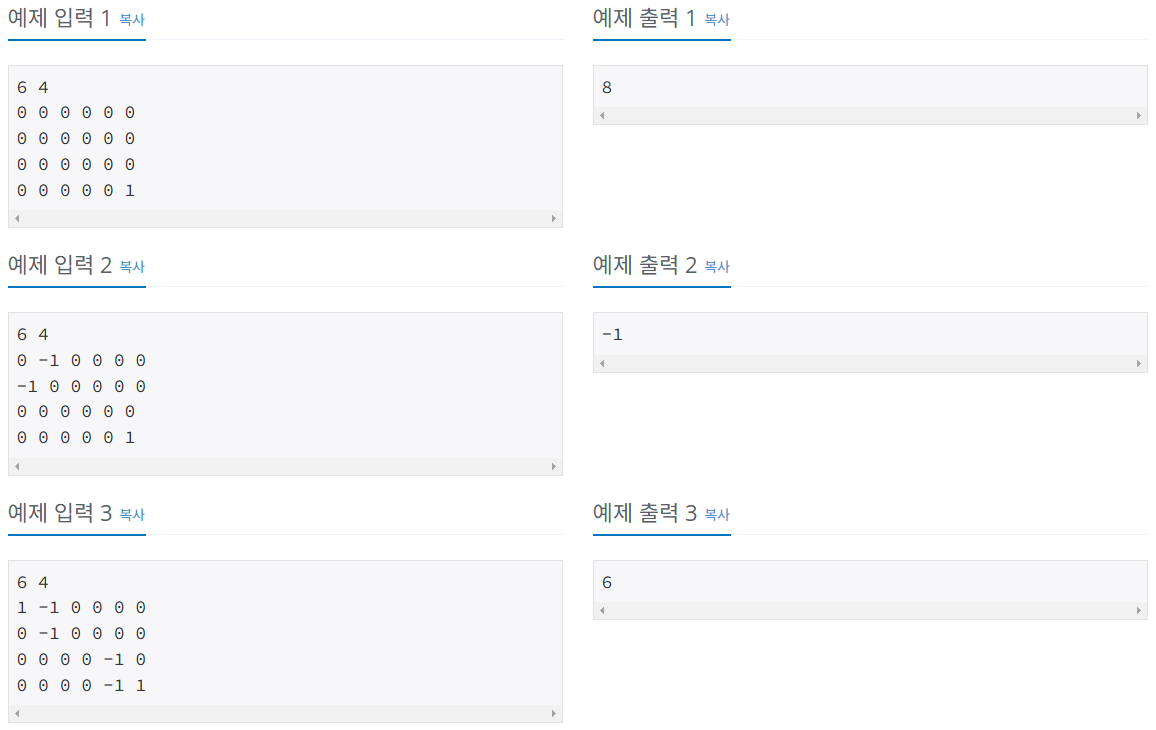
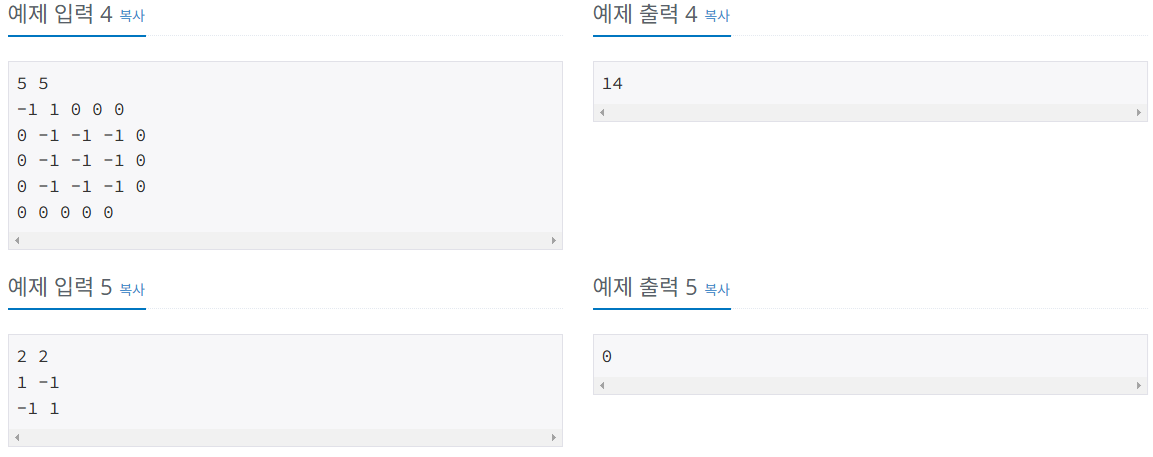
입출력 예
코드 구현
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int M, N;
vector<vector<int>> box;
queue<pair<int, int>> rtomato; //익은 토마토 시작 좌표 저장
int dx[4]={-1, 1, 0, 0};
int dy[4]={0, 0, -1, 1};
int BFS(){
int x=0, y=0; //마지막 토마토 좌표 저장
while(!rtomato.empty()){
x = rtomato.front().first;
y = rtomato.front().second;
rtomato.pop();
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
int nx = x+dx[i];
int ny = y+dy[i];
if(nx>=0 && nx<N && ny>=0 && ny<M && box[nx][ny]==0){
rtomato.emplace(nx, ny);
box[nx][ny]=box[x][y]+1; //하나씩 익을수록 하루를 더해준다.
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
for(int j=0; j<M; j++){
if(box[i][j]==0){ //익지 않은 토마토가 남아있으면
return -1;
}
}
}
return box[x][y]-1; //시작날 제외
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin >> M >> N;
box.resize(N, vector<int>(M));
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
for(int j=0; j<M; j++){
cin >> box[i][j];
if(box[i][j]==1){
rtomato.emplace(i, j);
}
}
}
cout << BFS();
return 0;
}
시작점이 여러 개인 BFS 문제도 기존의 BFS 방식과 동일하게 해결할 수 있었다.
먼저 모든 시작점을 큐에 미리 넣어준 후, 일반적인 BFS 과정을 진행하면 된다.
출처: 백준, https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7576
